Just as electrification transformed factories and computers redefined offices, AI is reshaping how decisions are made, how products are built, and how people work and learn. Today, it is difficult to find an industry untouched by AI – whether through visible tools like chatbots and copilots, or invisible systems powering recommendations, forecasts, and optimizations behind the scenes.
If you are looking for reliable data on adoption, frequency of use, and business integration, this guide brings together the most significant AI usage statistics in one structured, practical resource.
- Global market value: The AI market is valued around $290–300 billion in 2025.
- Business adoption: Approximately 75–80% of companies worldwide report using AI.
- Daily engagement: Estimates suggest that 100M+ people use generative AI daily.
- Workforce impact: AI is expected to displace tens of millions of jobs by 2030, and create new roles, particularly in data, engineering, and AI operations.
Let’s unpack these figures in detail: from market size and adoption rates to practical steps for getting started with AI or scaling what you already have.
Understanding the AI Landscape in 2025
Before diving into market data, it helps to understand what “using AI” actually means today. The technology has evolved far beyond simple chatbots into a diverse ecosystem of tools that power modern life.
Types of AI You Encounter Daily
- Generative AI: Tools like ChatGPT, Claude, and Midjourney that create new content (text, code, images) from simple prompts. This is the most visible form of AI for consumers today.
- Predictive AI: Systems that forecast future outcomes based on historical data. This powers your Netflix recommendations, stock market trading algorithms, and weather apps.
- Computer Vision: Technology that “sees” and interprets images. It’s used in facial recognition to unlock your phone, quality control on factory lines, and self-driving car navigation.
- Agentic AI: The newest frontier for 2025 – autonomous “agents” that don’t just chat but do things. Instead of just writing a travel itinerary, an agent can book the flights, reserve the hotel, and add it to your calendar without human help.
Top 10 Enterprise AI Platforms Comparison
Organizations are moving away from “one-size-fits-all” models, instead choosing specific platforms that align with their security needs and technical stack.
| Rank | Platform | Best For | Key Feature | Pricing Model |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Microsoft Azure AI | Enterprise Integration | Native integration with Microsoft 365, Teams, and Windows. | Consumption + Seat License |
| 2 | OpenAI (ChatGPT Ent.) | General Reasoning | Access to “o1” and “GPT-5” class models with best-in-class logic. | Per User / Per Token |
| 3 | Google Cloud AI | Data & Analytics | Deep integration with BigQuery and Gemini’s massive 1M+ token context window. | Consumption |
| 4 | AWS SageMaker | Builders & Devs | Full control over model training, fine-tuning, and deployment. | Consumption (Compute) |
| 5 | Anthropic (Claude) | Safe/Human-like Tasks | Large context windows and a focus on “constitutional” safety for sensitive ops. | Usage / Token |
| 6 | UiPath | Process Automation | Combining AI with RPA to click buttons and fill forms in legacy software. | License / Bot |
| 7 | Salesforce Einstein | CRM & Sales | AI embedded directly into customer data (no setup required). | Included / Add-on |
| 8 | GitHub Copilot | Software Engineering | The standard for autocomplete, debugging, and code explanation. | Per User ($19/mo) |
| 9 | Databricks MosaicML | Data Engineering | Training custom, private models on your own proprietary data. | Consumption |
| 10 | Midjourney | Creative & Design | Industry-leading image generation quality for marketing assets. | Subscription |
Feature Matrix: Which Tool for Which Task?
Selecting the right tool depends entirely on the specific outcome you need. In 2025, the “best” model is the one specialized for your use case.
- For Coding & Engineering: GitHub Copilot remains the gold standard for autocomplete, while Claude 3.5 Sonnet is increasingly favored by senior engineers for complex architectural reasoning and debugging.
- For Writing & Strategy: Claude is widely preferred over GPT-4 for long-form writing because it captures nuance better and sounds less “robotic.” Its large context window allows it to read entire books or legal contracts in one go.
- For Data Privacy: Azure AI and AWS SageMaker are the only choices for regulated industries. Unlike consumer tools, they offer “zero-data retention” guarantees, ensuring your proprietary data never trains the public model.
- For Complex Automation: UiPath combined with generative AI is the solution for “messy” workflows. It can read a PDF invoice (AI), extract the data (AI), and then log into a legacy SAP system to type it in (RPA) without human intervention.
While these tools are diverse, they all share a common limitation that defines the current technological moment.
The Current State of Capability
While we haven’t reached “Artificial General Intelligence” (AGI) – machines that can think exactly like humans across any domain – today’s “Narrow AI” is exceptionally powerful in specific tasks. Current models can pass medical licensing exams, debug complex software code, and generate photorealistic video, but they still struggle with common-sense reasoning and can occasionally “hallucinate” (invent facts).
Despite these limitations, adoption is accelerating because the utility now outweighs the novelty. For businesses and individuals alike, AI has become a “force multiplier” – a tool that doesn’t necessarily replace human effort but drastically amplifies what one person can achieve in a day.
Global AI Market Overview
To grasp the specific numbers, let’s first overview the economic environment surrounding AI. Market size and investment trends indicate just how seriously industries and governments are betting on AI as a long-term driver of growth.
Market Size in 2025
Most recent market estimates put the global AI market (software, services, and specialized hardware) at roughly 290–300 billion USD in 2025, with many forecasts projecting it to reach around 1–1.3 trillion USD by 2030 and over 1.7 trillion USD in the early 2030s, implying a sustained 25–30% compound annual growth rate over the coming decade.
While methodologies vary, a typical consensus looks like this:
| Year | Estimated global market size | Context |
|---|---|---|
| 2023: The “Hype” Phase | ~$200–220 billion | Growth driven by experimental pilots and massive hardware purchases (GPUs) rather than software revenue. |
| 2024: The “Pilot” Phase | ~$240–260 billion | Early enterprise adoption of copilots; companies testing use cases but hesitating on full deployment due to accuracy risks. |
| 2025: The “Integration” Phase | ~$290–300+ billion | AI moves from a standalone experiment to a core component of existing software stacks (e.g., Salesforce, Microsoft 365), driving recurring revenue. |
| 2030 (forecast): The “Utility” Phase | ~$1.0–1.3 trillion | AI becomes invisible infrastructure, much like cloud computing is today. |
| 2032–2035 (forecast): Mature Market | ~$1.7+ trillion | Growth stabilizes as market saturation increases; value shifts from building models to specialized vertical applications. |
The estimates discrepancy comes from what is being counted. Lower estimates typically track only AI software revenue, while higher estimates (like the one above) include the massive expenditure on AI hardware infrastructure (chips, data centers) and consulting services required to implement these systems.
AI Market Layers
This $300 billion valuation is composed of four distinct layers:
- Core platforms and models (~30%): The foundation layer. This includes revenue for model providers (like OpenAI, Anthropic) and the cloud compute required to run them (Azure, AWS, Google Cloud).
- Enterprise applications (~25%): The application layer. This is not “new” AI software, but rather the AI premium charged on existing platforms—for example, the extra cost for “Salesforce Einstein” or “Github Copilot” within a standard subscription.
- Vertical solutions (~20%): Industry-specific tools. Unlike broad chatbots, these are highly specialized (e.g., an AI tool purely for detecting breast cancer in radiology or spotting money laundering in banking).
- Services & Implementation (~25%): The human layer. A massive portion of the current market value is actually paid to consulting firms (like Deloitte or Accenture) to help legacy companies clean their data and integrate these tools safely.
Growth Drivers and Segments
Expert Insight: “The center of gravity for AI is shifting from model building to model application. The winners in 2025 are not just the companies training the biggest models, but the enterprises figuring out how to weave them into the messy reality of daily business operations.” — Senior Analyst, Gartner
Several distinct engines are powering this expansion:
- Generative AI and copilots: Tools generating text, code, images, and audio are now standard for developers, marketers, knowledge workers, and students.
- Industry-specific AI: Sectors like healthcare, finance, and manufacturing are investing in specialized solutions tailored to their regulatory needs and data environments.
- Enterprise automation: Large organizations are embedding AI into core systems like ERP, HRIS, and supply chain platforms to support decision-making.
- Infrastructure and chips: Training and running large models requires specialized hardware and optimized data centers, driving massive investment in compute capacity.
These segments explain why some roles report higher adoption than others: functions like coding, content creation, and customer support benefit from more mature tools with clearer ROI.
Investment Trends and Capital Flows
“We are seeing a massive ‘graduation’ of pilots. In 2023, companies played with chatbots. In 2025, they are deploying customer service agents that handle real money and real data. The focus has shifted entirely to ROI.” — Bain & Company Executive Survey 2025
Capital is no longer flowing blindly into “anything with AI in the name.” In 2025, investors and CFOs have shifted their focus from promise to proof.
1. Venture Capital: The “Applied AI” Pivot
While total funding remains high (AI commanded over 50% of all global VC dollars in 2025), the target has shifted. Investors are increasingly skipping “wrapper” companies (thin interfaces built on top of ChatGPT) in favor of Vertical AI – startups solving deep, specific problems in law, biology, or manufacturing.
2. Corporate Spending: From “Science Fair” to Production
For the last two years, many corporate AI projects were stuck in “pilot purgatory” – fun experiments that never reached the real world. That has changed. In 2025, companies ranking AI as a top-three strategic priority rose from 60% to 74%.
3. Government Initiatives: The Race for “Sovereign AI”
Nations have realized that relying on foreign AI models is a national security risk. This has triggered a global arms race to build Sovereign AI clouds – government-owned infrastructure ensuring a country can train its own models on its own data/laws.
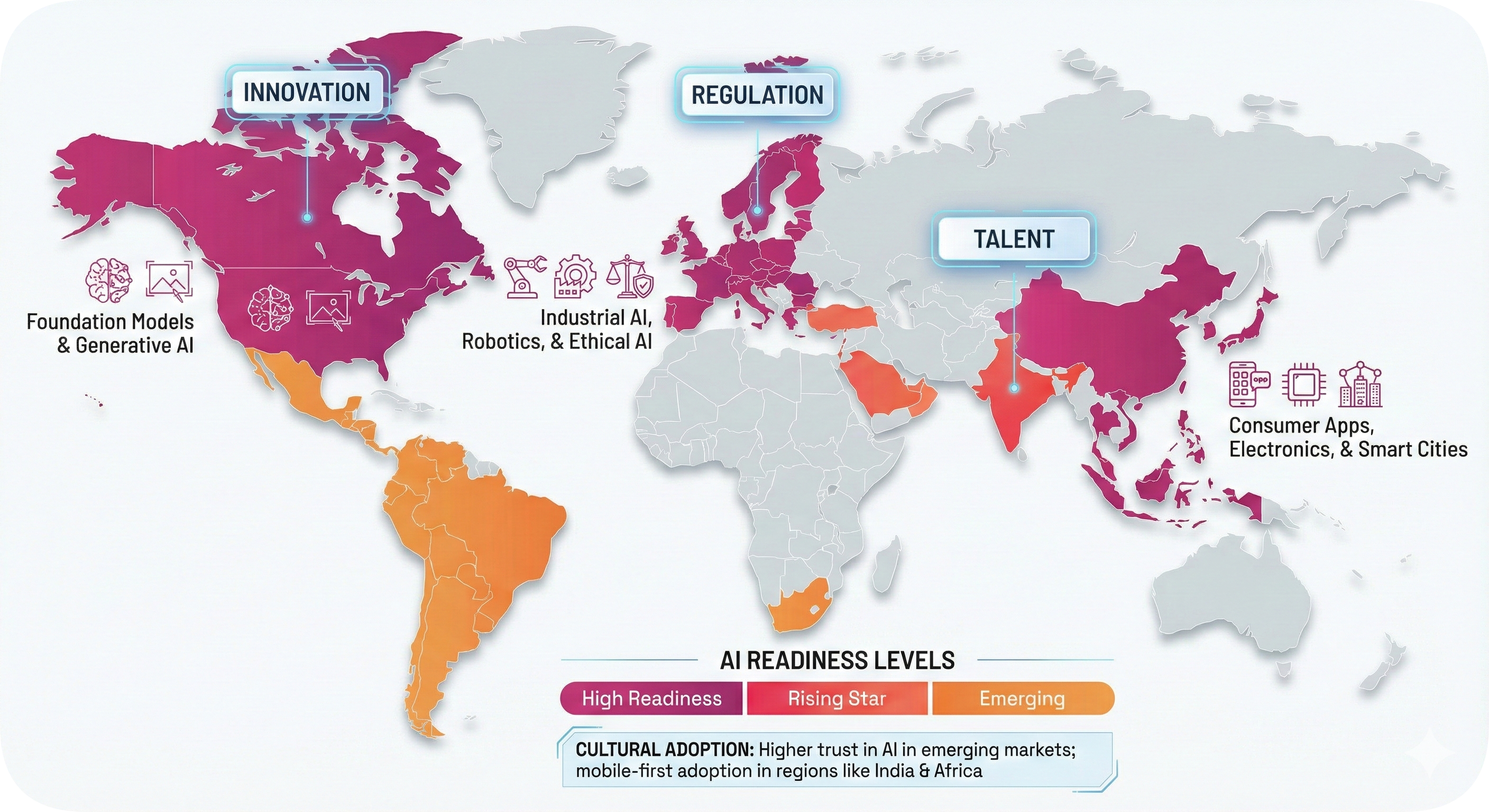
Country-level Leadership and Readiness
AI development is not evenly distributed. While the US and China dominate in raw power (compute, capital, and research), smaller nations like Singapore and the UK are carving out leadership roles by creating safer, faster regulatory environments for business.
Understanding these regional strengths is critical for multinational companies deciding where to pilot new AI initiatives.
TOP-5 Countries by AI Readiness Index
According to the Salesforce Global AI Readiness Index 2025, these are the nations that ranked highest in AI readiness:
| Rank | Country | Key Strength | Investment Focus |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | United States | Innovation Ecosystem | Model R&D, Enterprise Adoption |
| 2 | Singapore | Governance & Infrastructure | Smart City, Public Sector AI |
| 3 | United Kingdom | Talent & Safety | Fintech AI, AI Safety Research |
| 4 | Canada | Research Talent | Deep Learning, Health AI |
| 5 | Germany | Industrial Application | Manufacturing AI, Robotics |
Regional Archetypes
- The Scalers (USA & China): These nations lead in raw capabilities. The US dominates in generative model creation (OpenAI, Anthropic, Google), while China excels in real-world deployment, integrating AI into surveillance, manufacturing, and consumer super-apps at massive scale.
- The Regulators (European Union): The EU is positioning itself as the global “referee.” While adoption is slower due to strict privacy laws (AI Act), the region is a leader in Industrial AI (robotics, automotive) where safety is paramount over speed.
- The Accelerators (Singapore, UAE, India): These nations view AI as a national imperative to leapfrog economic barriers. Singapore and the UAE lead globally in workforce adoption (60%+ monthly usage), driven by government mandates to become “AI-first” nations. India is rapidly becoming the world’s AI talent hub, projected to surpass the US in developer count by 2030.
AI Adoption and Usage Rates
With the market context established, we can address the core questions: how many people are actually using these tools, how often do they use them, and how deeply have businesses integrated them?
Individual Adoption: How Often Is AI Used Globally?
From a user’s perspective, counting how many people use AI daily is complex because interactions are often seamless. People engage with AI when a navigation app reroutes them around traffic, a streaming service suggests a new series, a bank flags a suspicious transaction, or a student asks a chatbot to clarify a concept.
Intentional Use of AI-driven Tools
- Cumulative users: Well over 1.5–2 billion individuals have used generative AI at least once.
- Regular users: Approximately two-thirds of those say they use AI tools at least once a month.
- Frequent users: Depending on the definition, 20–30% of adults in digitally advanced markets engage with generative AI weekly or more.
This indicates that AI has achieved mainstream awareness and substantial regular use, particularly in knowledge work, education, and creative fields.
Daily engagement: How Many People Use AI Daily?
To understand the true scale of AI, we must look beyond simple signup numbers and examine daily habits. Two distinct behaviors define the current landscape:
Direct Usage
Over 122 million people now use distinct generative AI tools (like ChatGPT or Gemini) every single day to write, code, or create. This usage is heavily concentrated in North America, Europe, and parts of Asia, and among students, developers, marketers, and knowledge workers.
Indirect Usage
When accounting for embedded AI (such as Netflix recommendations, Spotify playlists, or Gmail autocomplete), the majority of internet users interact with AI algorithms dozens of times daily, often without realizing it.
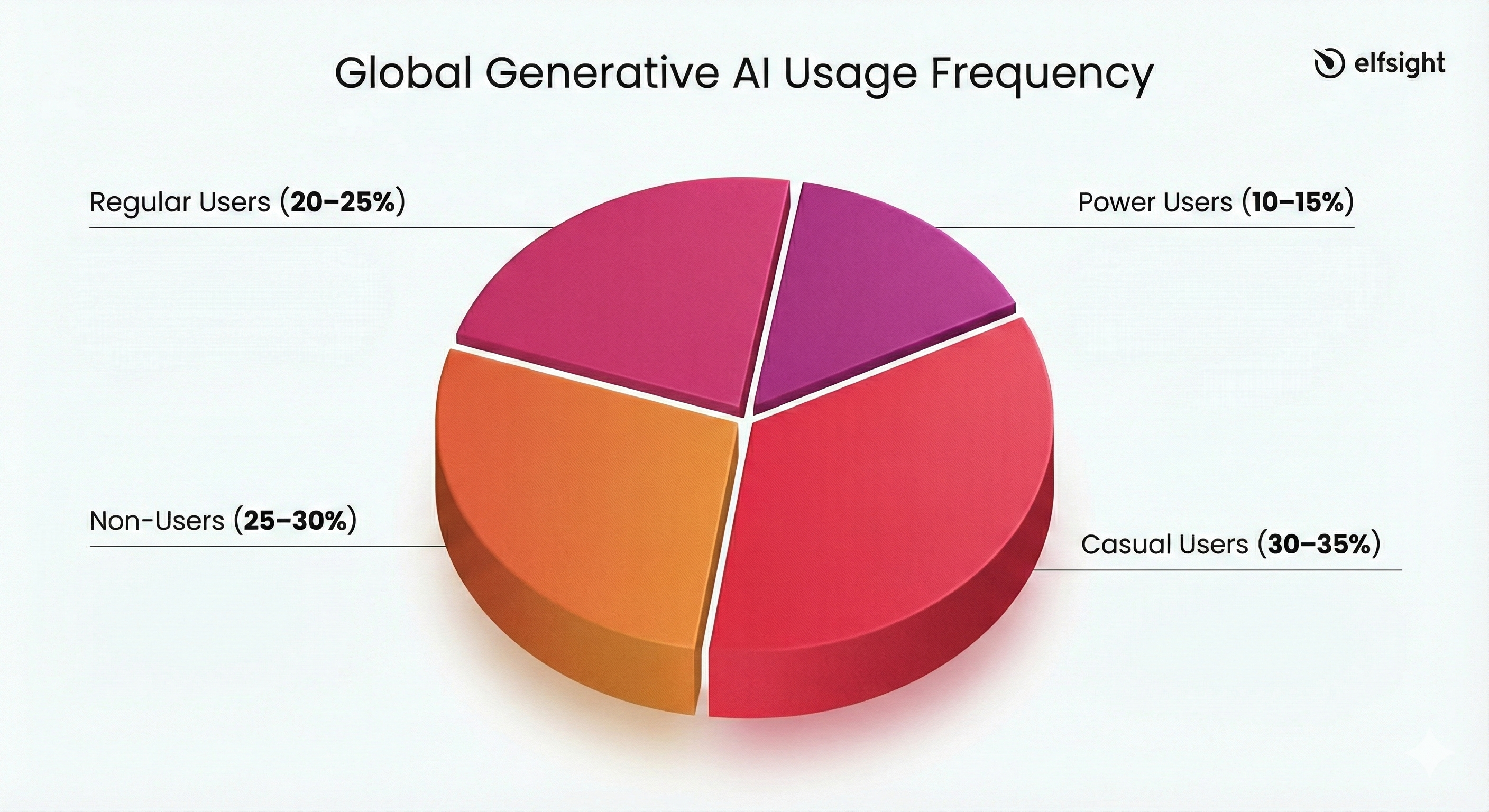
Frequency of Generative AI Usage by Online Adults
Below is a conservative global estimate for 2025 that focuses on explicit generative AI tools:
| User Segment | Usage Frequency | Typical Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Power Users (10–15%) | Multiple times daily | Professional coding, copywriting, academic research, and complex problem-solving. |
| Regular Users (20–25%) | Weekly | Drafting emails, summarizing documents, planning travel, or creative brainstorming. |
| Casual Users (30–35%) | Monthly / Ad-hoc | One-off questions, generating fun images, or testing specific features out of curiosity. |
| Non-Users (25–30%) | Rarely / Never | Older demographics or regions with limited access to high-speed internet. |
While “everyone” has heard of AI, daily reliance is still concentrated among students and knowledge workers. However, as AI features are seamlessly integrated into operating systems (Apple Intelligence, Windows Copilot), this distinction will vanish – soon, “using AI” will be, in a way, synonymous with simply using a computer.
Business Adoption: How Many Companies Use AI?
For organizations, the question is no longer if they should use AI, but where. In 2025, adoption has matured from experimental “science fair” pilots to strategic deployments focused on measurable ROI. Companies lagging behind now face a tangible productivity gap compared to competitors who have successfully automated routine operations. Current market data reveals a clear divide based on company size:
- Widespread Integration: Approximately 78% of all organizations report using AI in at least one business function today.
- The “Scale” Gap: While large enterprises are deploying complex custom models, small businesses struggle with implementation costs, often limiting their adoption to off-the-shelf tools like ChatGPT.
Enterprise Adoption Rates by Company Size (2025)
| Company Size | Adoption Rate | Primary Barrier to Growth |
|---|---|---|
| Enterprise (10k+ employees) | 87% | Governance: Managing data privacy, security, and internal compliance across thousands of users. |
| Mid-Market (250-9,999 employees) | 75% | Talent: Difficulty hiring specialized AI engineers to build custom solutions. |
| Small Business (<250 employees) | 39% | Cost & Time: Lack of budget for dedicated tools and no time to train staff on new workflows. |
Source: SecondTalent Enterprise Adoption Report 2025 & OECD SME Outlook
We are witnessing a “two-speed” adoption economy. Large firms are racing ahead with custom AI integrations, while smaller businesses are just beginning to scratch the surface. To bridge this gap, the market is shifting toward cheaper, pre-packaged AI tools that require zero coding to implement.
Adoption Timeline: From Experimentation to Integration
To understand where AI is going, we must look at how quickly it has matured. In just five years, we have moved from “lab research” to “business-critical infrastructure.”
- Pre-2020 (The Research Era): AI was the domain of data scientists. Usage was limited to specialized recommendation engines (Netflix, Amazon) and academic research.
- 2020–2022 (The Pilot Era): Early adopters began testing “Classic AI” for backend tasks like fraud detection and simple chatbots. Usage was siloed within IT departments.
- 2023 (The Generative Explosion): ChatGPT brought AI to the masses. Adoption became “bottom-up” as employees started using tools secretly (Shadow AI) to write emails and code.
- 2024 (The Integration Phase): AI moved from a “side tab” to the “core app.” Microsoft Copilot, Gemini for Workspace, and Apple Intelligence embedded generative features directly into Word, Docs, and iPhones.
- 2025+ (The Agentic Era): The current frontier. We are shifting from chatbots (that answer questions) to agents (that perform actions). An agent doesn’t just write a travel itinerary; it books the flight, reserves the hotel, and adds it to your calendar.
Key Milestones in the AI Era (2020–2025)
To understand the current landscape, it helps to see how rapidly the ecosystem has evolved from experimental models to mass-market utilities.
| Year | Phase | Major Product Launches & Events |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | The Foundation | GPT-3 Released (OpenAI): The first model to demonstrate that AI could write human-like paragraphs, sparking the initial wave of “generative” startups. |
| 2022 | The Breakthrough | ChatGPT (November): The “iPhone moment” for AI. It reached 100 million users in two months, the fastest consumer adoption in history. Midjourney v1 (July): AI image generation becomes accessible to non-artists via Discord. |
| 2023 | The Explosion | GPT-4 (March): A massive leap in reasoning and coding ability. Microsoft Copilot (November): AI integrated directly into Word, Excel, and Windows, marking the start of enterprise adoption. Claude 2 (Anthropic): Introduced “safe” AI design and large context windows (reading entire books at once). |
| 2024 | The Integration | EU AI Act (May): The world’s first comprehensive AI law is passed, categorizing AI by risk level. Sora & Gemini 1.5: AI expands into high-fidelity video generation and massive multimodal understanding. |
| 2025 | The Agentic Era | GPT-5 (August): A step-change in reasoning, described as “a crucial advancement toward AGI.” Gemini 3.0: Google’s silent ecosystem upgrade, integrating advanced reasoning across all Workspace apps. Sovereign Clouds: Nations like Canada and India launch multi-billion dollar state-owned compute clusters to reduce reliance on US tech. |
Industry Deep Dives
Not all sectors adopt AI at the same speed or in the same way. While technology and financial firms have integrated AI into their core operations, others like healthcare and manufacturing are navigating strict regulations and legacy infrastructure. The following sections examine usage patterns across key industries.
Healthcare: Diagnosis, Workflows, and Patient Experience
Healthcare faces high stakes and strict regulations, yet it shows some of the clearest potential for economic and human impact. Adoption here has moved from cautious experimentation to strategic necessity, driven by massive staff shortages and rising administrative costs.
Adoption Trends
- 78% adoption rate among major healthcare networks for at least one AI application.
- CAGR of 36.8% in AI market growth, making it one of the fastest-expanding sectors.
- In advanced markets, over 50% of patients are now comfortable with AI assisting in their diagnosis, provided a human doctor makes the final decision.
Top 3 Use Cases
- Medical Imaging (Diagnostics): AI models assist radiologists by highlighting suspicious areas in X-rays, MRIs, and CT scans. Algorithms can now detect anomalies with 90%+ accuracy, often catching issues earlier than human review alone.
- Predictive Analytics (Patient Management): Forecasting readmission risks or identifying patients at risk of sepsis or other complications based on real-time vitals and historical data.
- Revenue Cycle Management (Operations): Automating medical coding, billing, and claims processing to reduce administrative errors and accelerate reimbursement.
Healthcare ROI & Impact (2025)
| Metric | Average Impact | Typical Time to Value |
|---|---|---|
| Financial Return | $3.20 return for every $1 invested | 14 Months |
| Admin Efficiency | 30% reduction in documentation time | 3-6 Months |
| Clinical Speed | 40% faster diagnostic turnaround | 6-12 Months |
Finance: Risk, Fraud, and Algorithmic Decisions
The financial sector has used machine learning for years (e.g., for high-frequency trading), but generative AI is opening new frontiers in customer experience, fraud prevention, and back-office efficiency. Banks are aggressively deploying AI to combat sophisticated digital crime and personalize banking services.
Adoption Trends
- 89% adoption rate in financial services, one of the highest of any industry.
- 90% of financial institutions now use AI specifically to fight fraud and financial crime.
- 58% of firms attribute direct revenue growth specifically to their AI initiatives.
Top 3 Use Cases
- Fraud Detection & AML: Real-time systems analyze millions of transactions per second to identify anomalies. New AI models have reduced false positives by 20%, saving billions in operational costs and lost revenue.
- Algorithmic Trading: AI-driven models analyze market sentiment, news, and historical data to execute trades at speeds and volumes impossible for humans.
- Customer Service & Advisory: Advanced chatbots handle routine banking inquiries (balance checks, transfers) and offer personalized financial advice based on spending patterns.
Finance ROI & Impact (2025)
| Metric | Average Impact | Typical Time to Value |
|---|---|---|
| Fraud Savings | £9.6 billion saved annually (Global) | 3-6 Months |
| Accuracy | 90%+ fraud detection rate | Immediate |
| Support Volume | 20-30% reduction in call volume | 6-12 Months |
Manufacturing: Predictive Maintenance and Smart Factories
Manufacturing leverages AI to predict failures, optimize production, and ensure quality at scale. This sector is transitioning to “Industry 4.0,” where physical machines are digitally connected and intelligent, allowing factories to self-correct before issues occur.
Adoption Trends
- 68% adoption rate in the manufacturing sector.
- Predictive maintenance is the entry point for most firms, accounting for the largest share of AI spending.
- Growth is driven by the critical need to minimize costly unplanned downtime, which costs the industry $1.4 trillion annually.
Top 3 Use Cases
- Predictive Maintenance: Sensors monitor vibration, temperature, and sound to forecast when equipment will fail before it happens, allowing for just-in-time repairs.
- Visual Quality Inspection: Computer vision systems inspect products on the assembly line for microscopic defects, scratches, or assembly errors at speeds humans cannot match.
- Supply Chain Optimization: AI analyzes weather, demand surges, and shipping data to predict inventory needs and optimize logistics routes.
Manufacturing ROI & Impact (2025)
| Metric | Average Impact | Typical Time to Value |
|---|---|---|
| Downtime | 30-50% reduction in unplanned stops | 9-12 Months |
| Maint. Costs | 20-40% reduction in repair spend | 12+ Months |
| Quality | 98%+ defect detection accuracy | 3-6 Months |
Marketing and Sales: Personalization at Scale
Marketing is one of the fastest-moving areas for AI usage. Generative AI has fundamentally changed the economics of content creation and personalization, allowing small teams to produce enterprise-level output.
Adoption Trends
- 89% of marketers report using AI tools in their workflows.
- Daily usage is common for tasks like copywriting, image generation, and email optimization.
- The focus has shifted from “automating everything” to “human-AI collaboration” to maintain authenticity in brand messaging.
Top 3 Use Cases
- Content Generation: Drafting blog posts, social media captions, ad copy, and generating visual assets. Tools like Jasper, Copy.ai, and Midjourney are standard.
- Hyper-Personalization: Tailoring email subject lines, landing page content, and product recommendations to individual user behaviors and preferences at scale.
- Campaign Optimization: analyzing ad performance in real-time to automatically reallocate budget to the best-performing channels and creatives.
Marketing ROI & Impact (2025)
| Metric | Average Impact | Typical Time to Value |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | 50% reduction in campaign creation time | Immediate |
| Engagement | 20-30% higher customer satisfaction (CSAT) | 1-3 Months |
| Sales | 1.7x higher conversion rates on personalized ads | 3-6 Months |
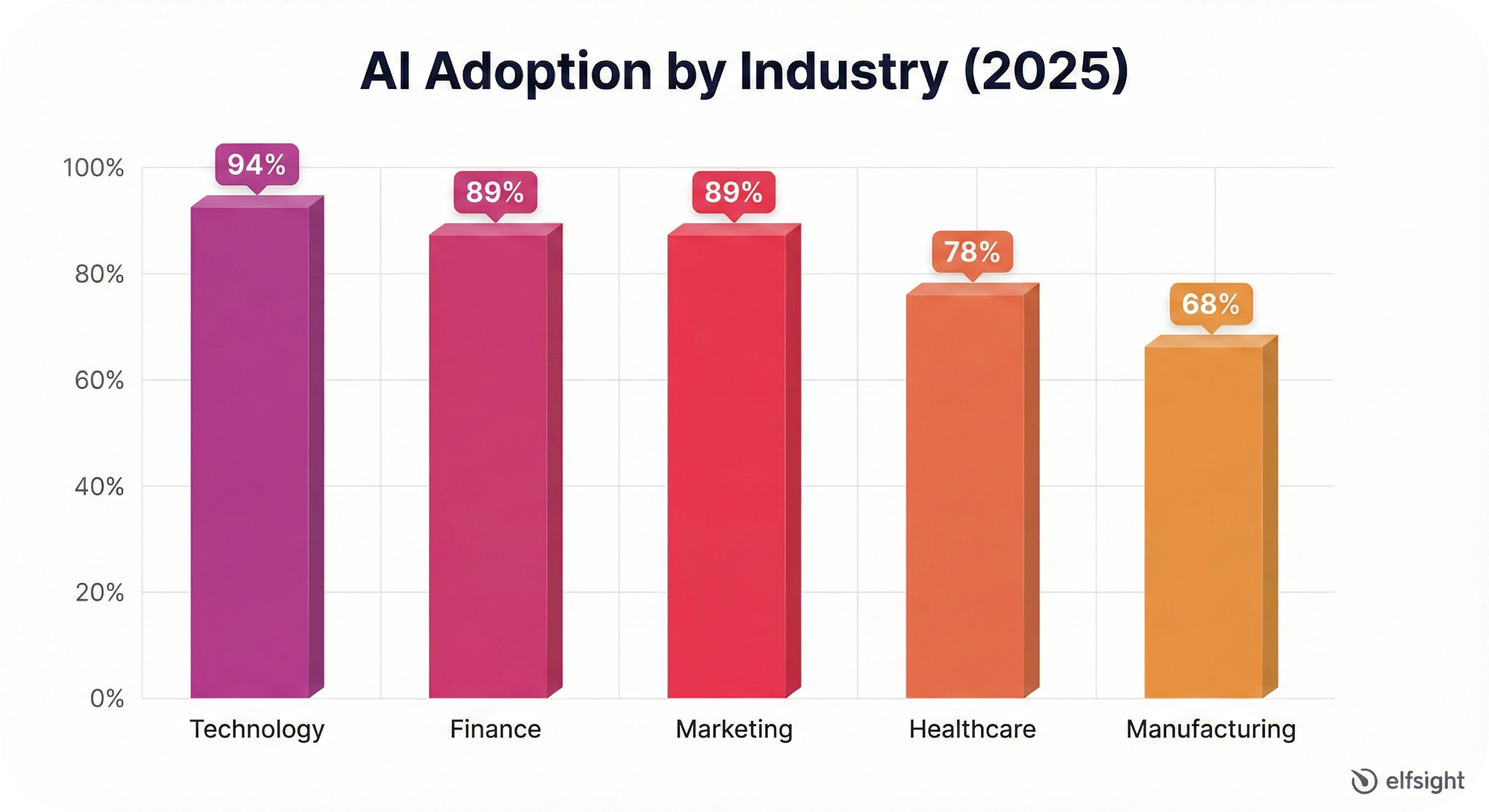
Industry Comparison: AI Metrics by Sector
While every industry is adopting AI, the speed and motivation differ wildly. Technology and Finance lead because their core product—data—is naturally suited for AI. In contrast, Manufacturing and Healthcare face physical and regulatory barriers that slow down initial rollout but offer deeper long-term value.
| Industry | Adoption Rate | Primary Driver | Top Barrier | Typ. ROI Timeline |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Technology | 94% | Innovation Speed | Talent Shortage | 3-6 Months |
| Finance | 89% | Risk/Fraud Reduction | Regulation | 6-12 Months |
| Marketing | 89% | Efficiency/Scale | Quality Control | 1-3 Months |
| Healthcare | 78% | Patient Outcomes | Data Privacy | 12-18 Months |
| Manufacturing | 68% | Uptime/Cost | Legacy Hardware | 9-15 Months |
Workforce Impact
“The gap between the AI-literate and the AI-illiterate workforce is widening faster than the education system can close it. In 2025, ‘AI literacy’ is the new ‘computer literacy’—a baseline requirement, not a bonus skill.” — Lead Economist, World Economic Forum
As we saw in the “Industry Deep Dives,” AI is not just a background tool—it is actively rewriting job descriptions in healthcare, finance, and marketing. This shift has sparked a global debate: will AI take jobs, or make them better? The data for 2025 points to a “churn,” where roles are not simply erased but transformed.
Job Displacement and Creation
Major labor market studies converge on a similar conclusion: while automation will eliminate routine roles, the efficiency gains will spark a massive wave of new, higher-value positions.
- Jobs Displaced: ~92 Million roles (primarily in data entry, basic administration, and routine assembly) are at risk of automation by 2030.
- Jobs Created: ~170 Million new roles (centered on AI maintenance, big data, green energy, and human-centric care) will emerge.
- Net Impact: A positive gain of ~78 Million jobs, though these roles will require vastly different skills than the ones they replace.
Salaries and Emerging Careers
The “AI Premium” is real. Workers with verified AI skills are seeing significant wage growth, while traditional tech roles face compression. As demand grows, compensation for AI-fluent roles remains strong:
- Wage Premium: Non-tech roles (like marketing or HR) that require AI skills now offer 28% higher salaries on average than identical roles without AI requirements.
- Tech Compression: Traditional IT support and junior coding roles are seeing salary stagnation as Copilots automate entry-level tasks.
- New Career Paths: Roles like Prompt Engineer, AI Ethicist, and Model Finetuner have moved from niche to mainstream, often commanding $150k+ starting salaries.
Skills Gap Analysis by Role
The shift in daily tasks creates a “skills gap” between what the current workforce can do and what AI-enabled workflows actually require.
| Role | Critical AI Skill Needed | Demand Trend | Reskilling Difficulty |
|---|---|---|---|
| Software Engineer | AI-assisted coding (Copilot/Cursor) | 🔥 Very High | Low (Natural extension) |
| Marketer | Prompt engineering & personalization | 🔥 Very High | Medium (New logic) |
| Data Scientist | LLM tuning & RAG architecture | 🔝 High | High (Complex math) |
| Customer Support | AI tool handling & complex resolution | 🔝 High | Medium (Soft skills focus) |
| HR Manager | AI-driven talent analytics | 🔜 Stable | Medium (Data literacy) |
| Legal Counsel | AI regulation & IP law | 🔝 High | High (Rapidly changing laws) |
| Designer | AI image generation/editing | 🔝 High | Medium (New workflows) |
| Executive | AI strategic vision & governance | 🔥 Very High | High (Business model shift) |
Future Predictions: The Agentic Era (2025–2030)
As AI becomes a commodity, its value is shifting from “knowledge” (what it can write) to “action” (what it can do). The next five years will be defined by the rise of autonomous agents and physical robotics, moving AI from a digital assistant to an active participant in the real economy.
Expert Forecasts: From Chatbots to Teammates
Top executives and researchers are no longer focused on model size; their attention has shifted entirely to real-world capability.
- “By 2027, AI won’t just be a tool we use; it will be a teammate we manage.” — Director of AI Research, Big Tech Firm.
This means the primary skill of the future will shift from “prompting” (telling an AI what to write) to “delegating” (assigning the AI a goal and then reviewing its multi-step work), effectively turning every knowledge worker into a manager. - “The cost of intelligence will drop to near zero. The value will shift to who has the best proprietary data.” — Venture Capitalist.
As powerful models become cheap commodities, the only defensible competitive moat will be a company’s unique, private datasets (like patient records or historical financial logs) used to fine-tune a general model for a specific task.
Innovation Timeline: From Code to Concrete
The progression from digital helpers to physical workers will happen faster than most expect.
| Year | Era | Key Development |
|---|---|---|
| 2025-2026 | The Agentic Era | AI moves from “chat” to “action.” Agents can autonomously plan travel, book meetings, and negotiate simple contracts without constant human help. |
| 2027-2028 | Physical AI | AI “brains” get robot bodies. Humanoid robots become commercially viable in warehouses, manufacturing, and elder care facilities. |
| 2029-2030 | Scientific Discovery | AI models solve complex problems in physics and biology, dramatically accelerating drug discovery and clean energy breakthroughs. |
Emerging Trends Radar
Beyond the hype, three silent trends are shaping the infrastructure of tomorrow. Small Language Models (SLMs) are bringing powerful AI directly onto laptops and phones, allowing for complex processing without an internet connection and ensuring privacy. At the national level, the race for Sovereign AI is driving countries to build their own state-owned compute clusters to protect national security and economic interests. Finally, within organizations, the continued use of unapproved tools (“Shadow AI“) is forcing IT departments to rapidly deploy governance platforms to prevent massive data leaks.
FAQ: AI Economy
Is the AI market currently in a bubble?
Will AI actually replace human creativity?
Why is there such a big gap between US/China and Europe?
What is the single biggest barrier to adopting AI right now?
How do I spot 'AI washing' in software products?
Is 'Sovereign AI' just a buzzword?
Final Thoughts: The Shift from Novelty to Necessity
By 2025, artificial intelligence has definitively crossed the chasm from a futuristic experiment to a foundational layer of the global economy. The statistics we’ve explored tell a consistent story: what began as a tool for tech giants has permeated every layer of business and society.
The clear winners in this new landscape are not just the companies building the models, but the individuals and organizations who are aggressively integrating them into mundane workflows. Whether it is a hospital using predictive analytics to save lives, a bank using algorithms to stop fraud in milliseconds, or a freelance writer using a copilot to double their output, the value lies in application, not just access.
The technology will continue to evolve rapidly, moving from today’s chatbots to tomorrow’s autonomous agents, but the time to build the infrastructure, skills, and governance to handle that future is now.